Lewy body dementia (LBD), a type of dementia, is second only to Alzheimer’s disease in prevalence. It mainly impacts people aged 50 and older. Recognizing its symptoms and progression is essential, as it significantly impacts both cognitive and physical abilities, profoundly affecting daily life and relationships. This blog will walk you through the potential signs, levels, and treatments for LBD.
What is Lewy Body Dementia?
Lewy body dementia (LBD) happens when abnormal protein deposits, referred to as Lewy bodies, build up inside the human brain. These clumps of protein can disrupt how the brain works. They affect different areas of the brain, leading to challenges with memory, movement, thinking abilities, mood, and behavior.
When Lewy, our bodies intervene with mental features; people with LBD would possibly neglect matters without difficulty or have hassle wondering really. They may also experience changes in movement, leading to difficulty walking or maintaining balance. Mood changes, along with depression or anxiety, also can arise. Additionally, their behavior could possibly be exchanged in surprising ways, inflicting confusion for both the person with LBD and their loved ones. Lewy bodies can also cause a range of different signs and symptoms. Other than this, the symptoms can sometimes also turn to seeing things that are not there (hallucinations) or acting out goals while slumbering (REM sleep conduct sickness).
Types of Lewy Body Dementia
Lewy Body Dementia (LBD) is a complex circumstance with two primary sorts. Each kind has its particular signs, symptoms, and progression. Understanding these variations is crucial for recognizing and dealing with the disorder. Here are the two primary styles of LBD:
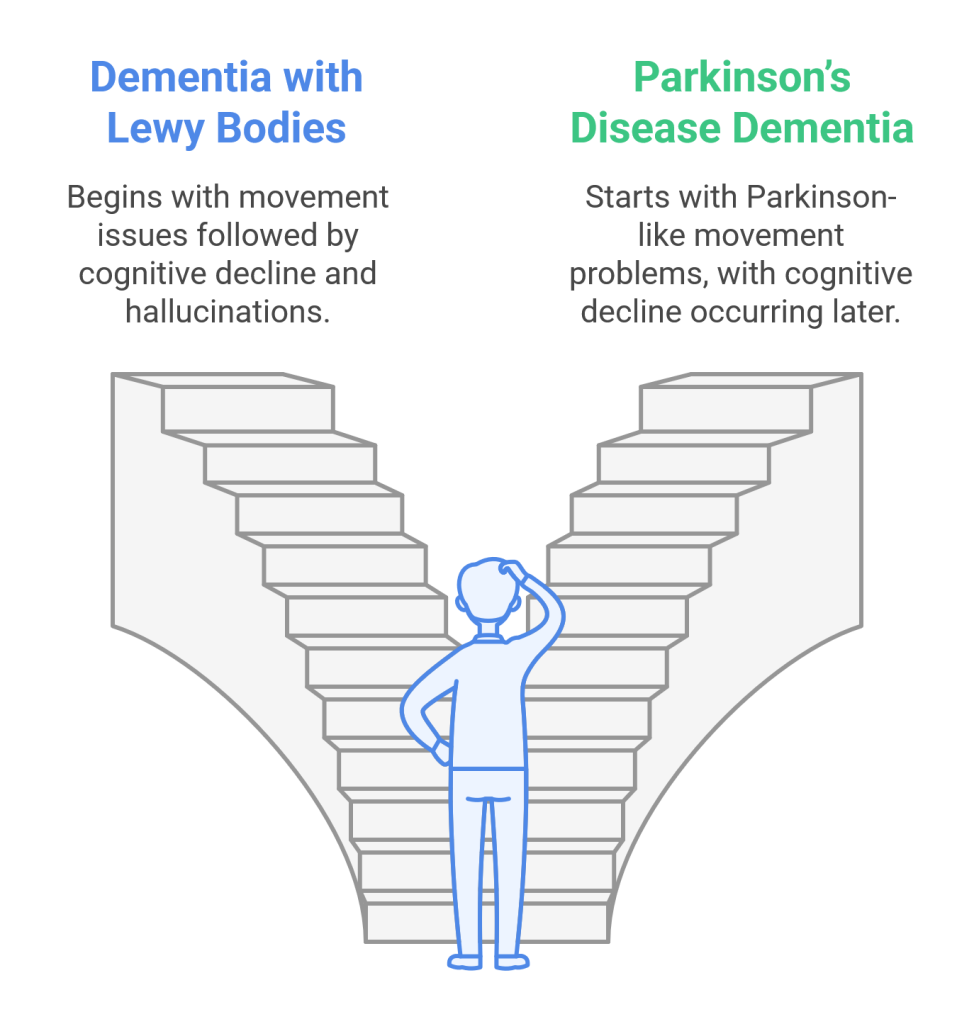
Dementia with Lewy Bodies (DLB)
This kind generally starts evolving with motion issues, which include stiffness or difficulty on foot. Within 12 months, individuals may additionally begin to have trouble with wondering and reminiscence, much like Alzheimer’s disease. They may also enjoy modifications in behavior and hallucinations, seeing matters that aren’t there.
Parkinson’s Disease Dementia (PDD)
This type starts evolving with motion problems, much like Parkinson’s disorder, like shaking and issues with coordination. Memory and questioning troubles develop an awful lot later because the disorder progresses.
Currently, there is no cure for LBD. However, treatments can help control the signs. Medications and healing procedures may enhance motion troubles, memory issues, and conduct changes. Researchers are facing challenges in understanding LBD better and how it differs from different situations. This study is essential for locating more powerful remedies in the future.
Lewy Body Dementia vs. Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease
Comparison with Alzheimer’s Disease
LBD and Alzheimer’s have some similarities. However, there are differences:
- Memory Loss: Alzheimer’s usually causes brief periods of memory loss early on, whereas LBD might not.
- Hallucinations: Hallucinations regularly arise in the first few years of LBD but are usually an overdue-degree symptom in Alzheimer’s.
- Thinking and Attention: Both diseases affect questioning, alertness, and interest; however, in LBD, those problems can differ.
Comparison with Parkinson’s Disease
LBD and Parkinson’s each purpose movement problems, together with stiff muscle tissue and tremors. However, in Parkinson’s, dementia generally takes place within the later ranges, if at all. In PDD (Persistent depressive disorder), cognitive issues seem plenty in advance. Additionally, one-of-a-kind medications are required to deal with LBD compared to Parkinson’s or Alzheimer’s.
Causes and Risk Factors
Causes:
Lewy bodies, named after the scientist who determined them, include a protein referred to as alpha-synuclein. When they are acquired, they disrupt the manufacturing of two essential chemicals inside the brain:
- Acetylcholine: Affects memory and mastering.
- Dopamine: Influences motion, temper, and sleep.
The precise motive of Lewy bodies’ buildup is unknown. Some genetic factors may additionally increase the threat, particularly adjustments within the genes APOE, SNCA, and GBA. While LBD is not commonly hereditary, having a member of the family with the ailment can increase your risk.
Risk Factors:
- Older Age: The likelihood of developing LBD increases with age.
- Health Conditions: Parkinson’s sickness and REM sleep conduct ailment can boost the risk.
- Family History: A family history of LBD can increase hazard.
- Gender: Those assigned male at the beginning are much more likely to develop LBD.
Symptoms of Lewy Body Dementia
Lewy Body Dementia (LBD) symptoms can vary widely among people and depend upon the precise form of LBD. Common symptoms fall into numerous classes, such as thinking capabilities, motion, sleep troubles, temper changes, and different physical signs. Understanding these symptoms can assist in recognizing the early signs and symptoms of LBD;
Thinking Skills
- Difficulty making decisions, judging distances, and paying interest.
- Problems with multitasking, making plans, organizing, or remembering.
- Hallucinations and confusion about time or vicinity.
Movement
- Shuffling or slow stroll and a frozen stance.
- Balance issues, stiff muscular tissues, and tremors.
- Reduced facial expression and smaller handwriting.
Sleep
- The aid of appearing out goals characterizes REM sleep conduct disorder.
- Excessive daylight sleepiness.
- Trouble falling or staying asleep.
Mood
- Depression, tension, and delusions.
- Agitation, irritability, and paranoia.
- Unusual behaviors like pacing or hand-wringing.
Other Symptoms
- Body temperature adjustments, dizziness, and blood stress problems.
- Sensitivity to temperature, urinary incontinence, and sexual dysfunction.
- Constipation and a weakened feeling of odor.
Early Signs of LBD
Hallucinations are often the first signal of LBD, affecting approximately 80% of human beings with the sickness. Other early symptoms encompass changes in wondering and problem-fixing, forgetfulness, sleep problems, motion difficulties, and mood modifications.
Stages of Lewy Body Dementia
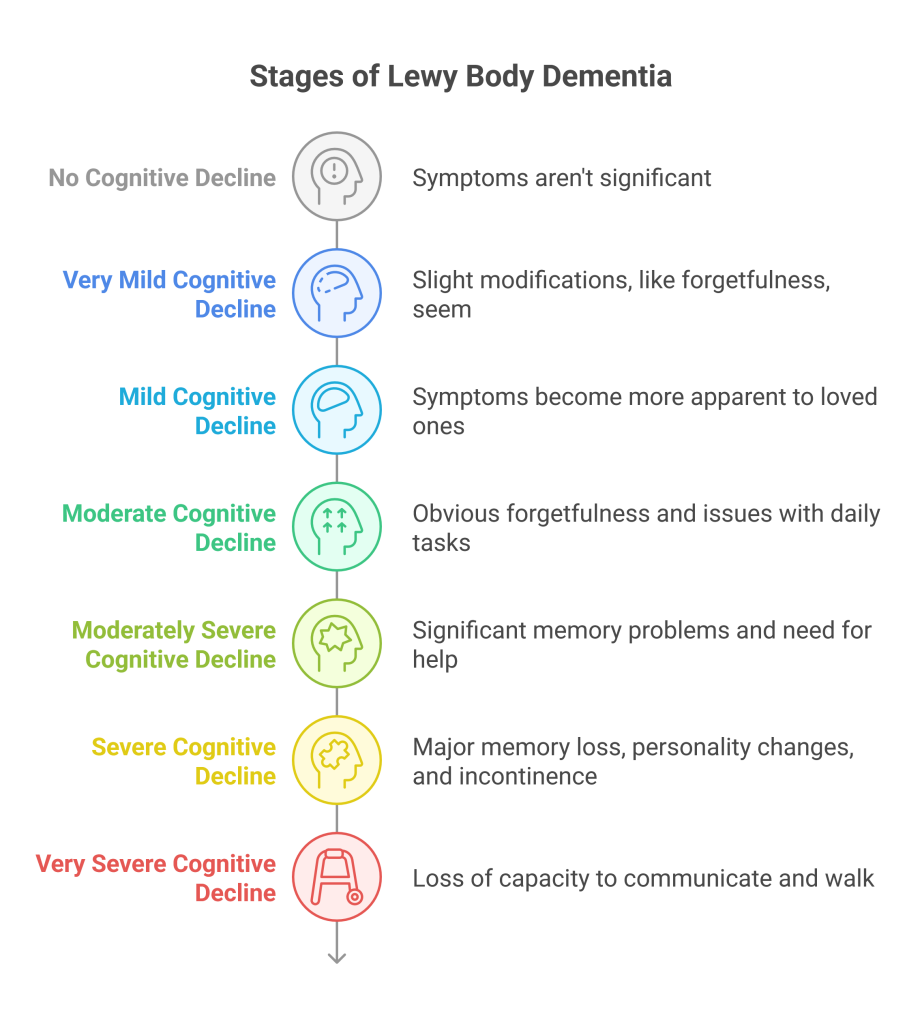
LBD progresses through seven distinct stages, each marked by different levels of cognitive decline and associated symptoms. Understanding those stages can assist patients, families, and caregivers in understanding adjustments and planning for destiny. The progression stages from no critical signs and symptoms to intense cognitive decline, affecting everyday lifestyles and communication.
- No Cognitive Decline: Symptoms aren’t significant.
- Very Mild Cognitive Decline: Slight modifications, like forgetfulness, seem.
- Mild Cognitive Decline: Symptoms come to be more apparent to loved ones.
- Moderate Cognitive Decline: Obvious forgetfulness and issues with daily tasks. Many diagnoses occur at this stage.
- Moderately Severe Cognitive Decline: Significant memory problems and need for help.
- Severe Cognitive Decline: Major reminiscence loss, character changes, and battle with incontinence.
- Very Severe Cognitive Decline: Loss of capacity to communicate and stroll, requiring significant help. This degree generally lasts 1.5-2.5 years.
Living with Lewy Body Dementia
Living with LBD affords many demanding situations for sufferers and their caregivers. To navigate those problems, it’s critical to build a sturdy support network, prioritize protection, plan for the future, focus on fun activities, and eat healthily to improve the patient’s brain health. These techniques can appreciably decorate the satisfaction of life for everyone worried. Here are a few guidelines for coping:
Create a Support Network
- Family and Friends: Rely on them for help and aid.
- Professional Help: Consider talking to a mental fitness expert or spiritual consultant.
- Professional Caregivers: As the sickness progresses, expert caregivers can be essential.
Take Safety Measures
- Medical Alert Services: These can provide emergency help at the frenzy of a button.
- Home Modifications: Install seize bars or ramps to save you from falls.
Plan Ahead
- Care and Financial Preferences: Discuss these with family and docs.
- Legal Documents: Consult an attorney to update your will and other critical documents.
- Future Services: Look into nursing or domestic care before you want them.
Treatment Options
While there is no treatment for Lewy Body Dementia (LBD), various treatments can assist in managing its symptoms. These include medications that enhance cognition and motion, non-medication treatment options for daily functioning and verbal exchange, and lifestyle modifications that promote usual well-being. Together, these procedures aim to beautify the best of existence for patients.
Medications
- Cholinesterase Inhibitors: Improve cognitive signs and symptoms by way of growing acetylcholine tiers.
- Levodopa: Helps with movement problems.
- Antipsychotic Medications: Used carefully to manipulate behavioral signs.
Non-Medication Therapies
- Physical Therapy: Helps with motion and balance troubles.
- Occupational Therapy: Assists with daily sports.
- Speech Therapy: Improves communique skills.
- Psychotherapy: Supports mental fitness and coping strategies.
Lifestyle Changes
- Regular Exercise: Enhances bodily and intellectual well-being.
- Healthy Diet: Supports usual health.
- Social Engagement: Participating in social sports can assist in keeping cognitive functions.
Wrapping Up
Lewy Body Dementia (LBD) is a complex sickness that affects many parts of a person’s life. Knowing the signs, stages, and remedy alternatives is vital for handling LBD. While there isn’t a remedy, specific healing procedures and lifestyle modifications can help reduce signs and symptoms. Building a sturdy guide community and planning for destiny is critical for patients and caregivers.
At Quail Crest, we recognize the challenges of living with LBD. Located in Redding, California, close to Caldwell Park and the Sacramento River, our community gives support and care to your needs. If you desire help, please get in touch with us to learn more about our services. Your well-being is our precedence, and we’re here to guide you each step of the manner.