Are you experiencing changes in your body, including muscle loss or trouble remembering things? These two issues usually happen together as you get older. Muscle loss causes your body to weaken and increases its chances of falling. In contrast, dementia affects your memory and judgment, so you can be less active and keep a schedule more easily. This lack of activity can lead to more loss of muscle, breaking the tough cycle.
The good news? You have control and manage both muscle loss and dementia. With exercise on a regular basis, a healthy diet, mental stimulation, and staying social, you can maintain both your body and mind in top form. By doing so, you are able to slow down the effects of these conditions, preserve your mobility, and stimulate your brain activity.
Let’s take a closer look and explore effective ways to manage muscle loss dementia.
The Link Between Muscle Loss and Dementia
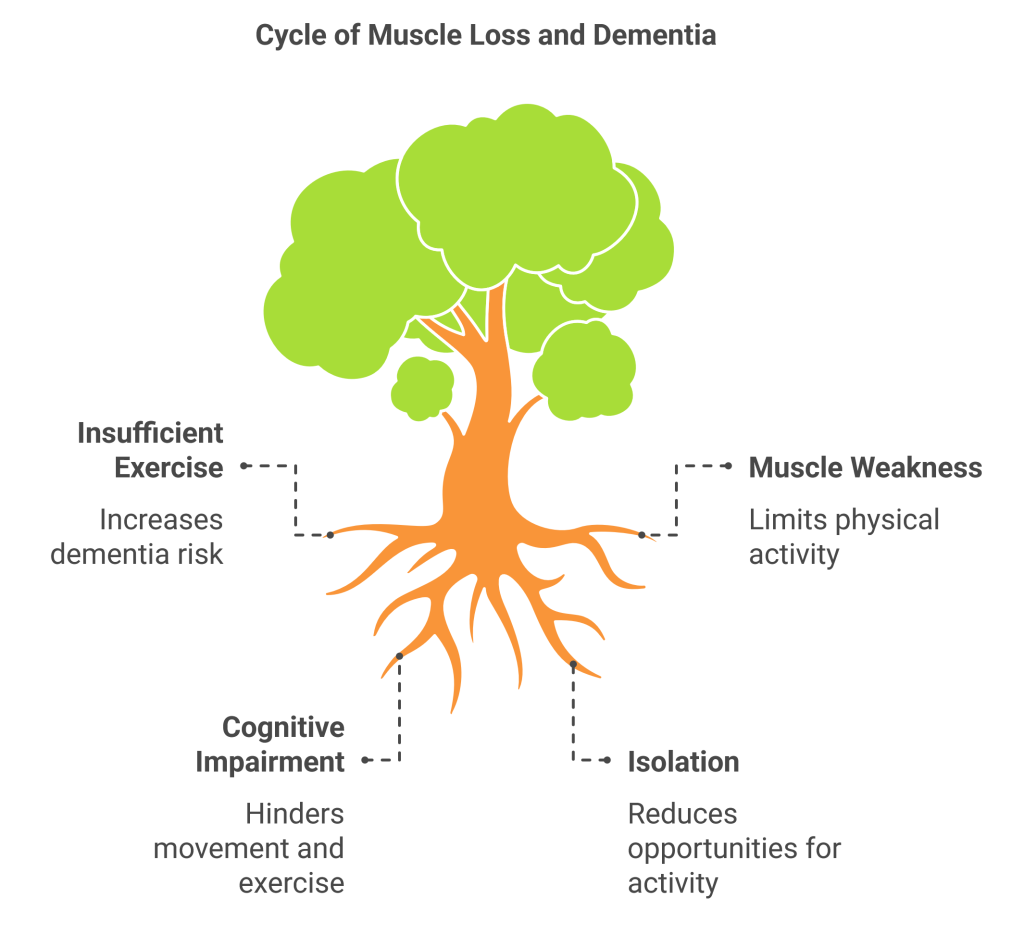
Scientists have proven that the link between muscle loss and dementia exceeds initial assumptions. Science indicates that insufficient exercise significantly raises dementia development risks throughout your lifespan. Strong muscles, alongside remaining active, lead to improved brain health as well as strengthened physical health.
Dementia creates barriers towards physical activity for people who suffer from it. The decline in muscle mass creates problems with physical movement, so people tend to become isolated and inactive. The cycle develops because weakening muscles cause an intensification of dementia symptoms, while cognitive impairment increases difficulty with physical activity.
Breaking this cycle is possible. Caring for your muscles and dementia combined will help you delay the deterioration or possibly stop its progression entirely in these areas.
How to Manage Muscle Loss and Dementia?
Managing muscle loss dementia is a crucial challenge as you age. Both conditions often go hand in hand; with muscle loss affecting mobility and dementia impairing cognitive function. The good news is that you can improve your overall well-being and maintain a higher quality of life, even as you face these challenges by:
Exercising Regularly
Exercising serves as an outstanding ability that benefits your body and your mind. It is the most efficient solution to fight muscle loss while promoting mental wellbeing, particularly during our elderly years. All types of physical movement count as exercise because they all serve to strengthen your muscles while improving your mood and boosting your memory function. Exercise presents a transformative benefit for dementia patients because it reduces their anxiety while improving their sleep quality and helps maintain their mental health. You should do exercises to:
- Exercises strengthen the muscles and promote overall body growth while your bone structure improves and reduces your chances of injury and accidental falls.
- Exercise raises blood flow through the body while supporting brain operations to establish better memory capabilities and overall health of the brain.
- Exercise creates better moods while lowering anxiety levels, thus benefiting people who have dementia.
- Better sleep becomes possible through exercise, which serves as a vital element for both mental health and physical health.
Perform strength-based exercises, aerobic workouts, and light physical activities, along with yoga, running, and various other types, to maintain an active body and an alert mind. Consult with both physical therapists and doctors who will help you design a customized exercise plan that is medically safe and enjoyable. Following activities you truly enjoy is the essential method to exercise success.
Eating a Balanced Diet
Nutrition affects the brain health of the patients. The proper management of muscle loss with dementia requires nutritional interventions. Muscle tissue reconstruction combined with maintaining strength is what protein specifically provides for the body.
The requirements for muscle health, together with cognitive operations, include proteins, specific vitamins, and minerals to function properly. Different vitamins exist in fatty fish, eggs, and dairy products, as well as fortified cereals.
Eating according to the Mediterranean dietary pattern represents an excellent approach to preserving your brain health. The human body requires sufficient hydration through water consumption alongside proper maintenance of bodily performance. Water intake control needs daily management since both muscle abilities and cognitive performance suffer from dehydration.
Stimulating Your Brain
Your brain requires mental activities just as your body needs physical movements to preserve proper brain health. Brain exercises through reading, puzzle activities, and memory play help to develop better cognitive abilities while fighting against dementia development.
The activities for dementia patients need to remain basic but satisfying. The brain benefits from activities that include both musical enjoyment and artistic hobbies, as well as time dedicated to closeness with loved ones. A key benefit of social connection is the reduction of isolation to maintain mental engagement.
Getting Enough Sleep
Sleep is crucial for both muscle recovery and brain health. During sleep, your body repairs muscle tissue, consolidates memories, and clears toxins from the brain. Poor sleep can make muscle loss dementia worse. For those with dementia, lack of sleep can lead to confusion, irritability, and worsening cognitive symptoms.
Setting a regular sleep schedule, avoiding caffeine in the afternoon, and calming your bedroom can help you sleep better. Doing relaxing things like reading or listening to soft music before bed can also help you unwind.
Staying Socially Engaged
Social interaction is key for both emotional and cognitive health. Loneliness and isolation can worsen dementia symptoms and lead to a decline in physical and mental health. Engaging with others through social activities, support groups, or hobbies gives you a sense of purpose and helps keep your mind active.
For people with dementia, staying connected with others is especially important to boost everyday care and communication. Family, friends, and caregivers provide support and can help encourage participation in group activities.
Seeking Professional Help
A team of healthcare providers should handle simultaneous dementia and muscle-loss management. Your healthcare provider, together with physical therapists and nutritionists, will develop distinctive plans that suit your needs. Monitoring professional appointments serves to examine advancements while needing modifications to your strategy.
Doctors provide medications to both treat dementia signs, along with the MD-related conditions that contribute to muscle deterioration. Your quality of life suffers less when you receive physical therapy combined with cognitive therapy.
Conclusion
Muscle loss dementia is a part of usual aging, yet you can manage this issue with appropriate care plans. A combination of regular physical activity, a balanced diet, brain exercises, sufficient rest, and social engagement can help prevent muscle loss in dementia, while also enhancing your overall quality of life.
There is no specific age to start prioritizing your mind and body, as it’s a vital habit for everyone. Be patient and stay dedicated to slow down muscle loss and reduce dementia symptoms, improving your overall quality of life. It’s important to maintain physical activity, stay socially connected, and seek support when needed. Taking consistent daily steps will help you build a stronger mind and body for the long term.
Contact Quail Crest Memory Care Community today to learn more about how to help your loved one live a healthier and more fulfilling life!